Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving overall health, particularly the immune system and energy levels, which are essential for seniors. As we age, the body's ability to fend off illnesses and maintain consistent energy throughout the day can diminish, making a well-balanced diet more important than ever.
Seniors often face several challenges that can impact their dietary habits and, consequently, their health. These challenges include changes in taste and appetite, difficulties with chewing or swallowing, and decreased mobility, which can make shopping and cooking more strenuous. Additionally, social isolation and the psychological impacts of aging can further complicate healthy eating habits.

Recognizing and addressing these dietary challenges is key to ensuring that seniors can enjoy a quality of life that is both active and vibrant. Proper nutrition not only supports immune function and energy levels but also plays a significant role in managing and preventing chronic diseases often associated with aging.
The Role of Nutrition in Supporting Immune Health
Nutrition plays a critical role in bolstering the immune system. Key nutrients that support immune function include:
- Vitamin C and E: These antioxidants protect immune cells from damage and aid their function.
- Vitamin D: Essential for immune defense, especially against respiratory infections, and often lacking in seniors.
- Zinc: Important for the development and communication of immune cells.
- Protein: Necessary for producing antibodies and immune cells.
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provides these vital nutrients, helping to enhance immune response, manage weight, and reduce inflammation, thereby supporting overall health and energy levels in seniors.
Key Nutrients for Senior Immunity and Energy
For seniors, specific nutrients are crucial for maintaining immunity and energy levels:
Vitamins
- Vitamin C: Enhances immune defense and reduces oxidative stress.
- Sources: Citrus fruits, bell peppers, and broccoli.
- Vitamin D: Boosts immune function and bone health.
- Sources: Fatty fish, fortified milks, and sunlight.
- Vitamin E: Protects cells from damage and supports immunity.
- Sources: Nuts, seeds, and leafy greens.

Minerals
- Zinc: Essential for immune cell function.
- Sources: Meat, shellfish, legumes, and nuts.
- Selenium: Antioxidant that supports immune response.
- Sources: Brazil nuts, seafood, and whole grains.
Other Key Nutrients
- Antioxidants: Combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Sources: Berries, dark chocolate, and beans.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Reduce inflammation and support brain health.
- Sources: Salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Protein: Vital for muscle maintenance and energy.
- Sources: Poultry, fish, dairy, and plant-based proteins like lentils.

Dietary Recommendations for Seniors
Addressing common senior health issues like difficulty chewing, reduced appetite, and altered taste senses requires thoughtful dietary adjustments. Here are practical tips and meal-planning ideas that incorporate essential nutrients while catering to these challenges.
Tips for Common Senior Health Issues
- Difficulty Chewing: Opt for soft-cooked or moist foods that are easier to chew and swallow. Examples include stews, braised meats, oatmeal, and smoothies.
- Reduced Appetite: Serve smaller, more frequent meals rather than three large ones. Focus on nutrient-dense foods to ensure adequate intake even when eating less.
- Altered Taste Senses: Enhance flavors with herbs, spices, and condiments to make meals more appealing without adding excessive salt or sugar.
Meal Planning Ideas
Breakfast
- Smoothie: Blend yogurt with a banana, a handful of spinach, flaxseeds, and a scoop of protein powder. This provides protein, omega-3s, and vitamins.
- Oatmeal: Cook with milk for extra protein and top with berries and a sprinkle of cinnamon to boost antioxidant intake.
Lunch
- Soup: Prepare a lentil soup with diced vegetables and chunks of soft-cooked chicken or turkey. This offers a good mix of protein, fiber, and minerals.
- Wrap: Use a soft whole grain tortilla filled with tuna or egg salad mixed with diced celery, lettuce, and avocado for healthy fats and protein.
Dinner
- Stew: Make a beef or chicken stew with potatoes, carrots, and peas. It's easy to chew and rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals.
- Baked Salmon: Serve with a side of mashed sweet potatoes and steamed spinach. Salmon provides omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D, while sweet potatoes and spinach offer fiber and vitamins.
Snacks
- Greek Yogurt and Honey: This combination offers calcium, protein, and a sweet flavor that can help with altered taste senses.
- Nut Butter on Toast: Provides a soft texture that’s easy to chew and is a good source of protein and healthy fats.
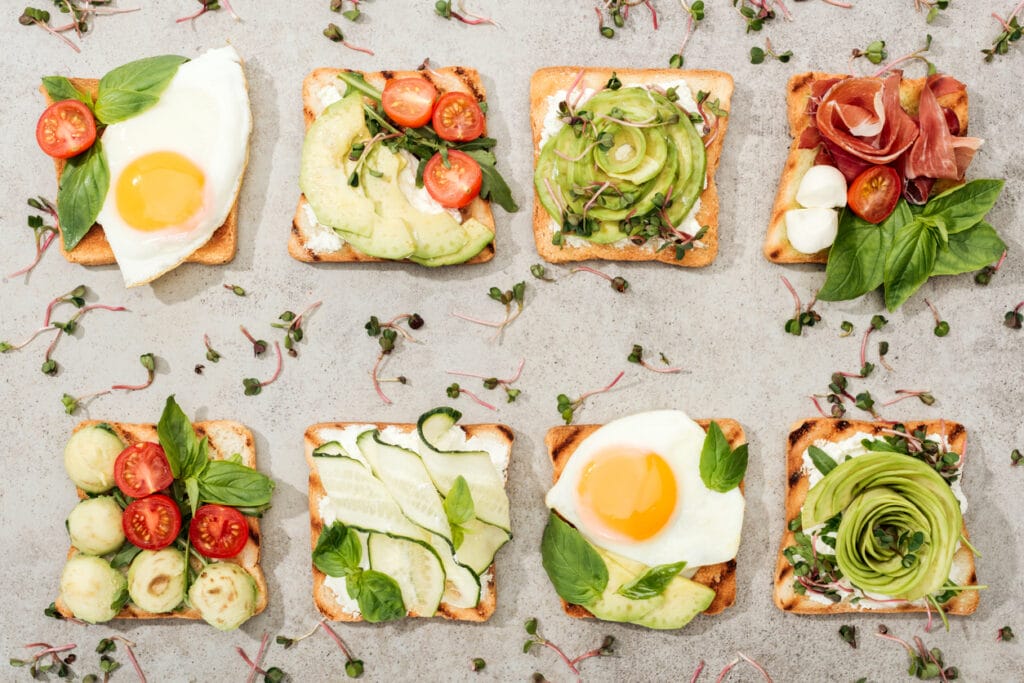

These meal options ensure that seniors can consume a balanced diet that addresses their specific health challenges while still incorporating essential nutrients for immune support and energy.
Supplements vs. Natural Nutrition
While a well-balanced diet is the best way to obtain essential nutrients, there are situations where supplements might be necessary to meet the specific health needs of individuals, especially seniors.
When Supplements Might Be Necessary
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Seniors with diagnosed deficiencies, such as vitamin D or B12, often due to limited dietary intake or absorption issues, may require supplements.
- Limited Sun Exposure: In cases where seniors aren't exposed to sufficient sunlight, supplementing with vitamin D is crucial to maintain bone health and immune function.
- Chronic Conditions: Certain conditions, like osteoporosis or age-related macular degeneration, may benefit from specific supplements like calcium or eye health formulas recommended by healthcare providers.
Importance of Consulting Healthcare Providers
Before starting any supplement regimen, it’s essential for seniors to consult with their healthcare providers. This step ensures that supplements will not interfere with existing medications or conditions. Healthcare providers can offer guidance based on a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s health profile.
Encouraging Natural Nutrition
Getting nutrients from food should always be the primary strategy because foods offer a complex matrix of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and other beneficial compounds that supplements cannot replicate. Foods in their natural form provide a balanced delivery of nutrients that the body can absorb and utilize efficiently. Here are a few reasons why natural nutrition is preferable:
- Synergistic Effects: Nutrients from food interact synergistically to enhance absorption and benefits. For example, iron from meat is better absorbed when consumed with vitamin C-rich foods like oranges or bell peppers.
- Additional Health Benefits: Whole foods contain fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals that contribute to overall health and can help prevent chronic diseases.
Practical Tips
- Diversify Diet: Encourage a variety of foods to cover different nutrients. Colorful fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats should be part of daily meals.
- Monitor Diet and Health: Regular check-ups can help detect any nutritional gaps, which can then be addressed either through diet adjustments or appropriate supplementation.
By prioritizing a nutrient-rich diet and considering supplements only when necessary and under professional guidance, seniors can optimize their health and well-being.
Lifestyle Factors That Support Nutritional Goals

Achieving optimal health, especially for seniors, goes beyond just a balanced diet. It encompasses a holistic approach that includes physical activity, proper sleep, and effective stress management. Each of these factors plays a crucial role in supporting immunity and maintaining energy levels.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for seniors as it helps boost the immune system, increases energy, and supports muscle strength and joint health. Activities like walking, swimming, or light aerobics are excellent options that also improve cardiovascular health and can enhance mood.
Sleep
Quality sleep is fundamental to good health. During sleep, the body repairs itself and regenerates its immune cells, which is crucial for fighting infections. Seniors should aim for 7-8 hours of good-quality sleep per night, maintaining a regular sleep schedule to support circadian rhythms and overall health.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and drain energy levels. Managing stress through mindfulness, meditation, or hobbies can improve mental health and boost physical well-being. Engaging in social activities and maintaining connections with family and friends also play a vital role in reducing stress and enhancing life quality.
Key Takeaways
Maintaining a strong immune system and high energy levels in seniors involves more than just a good diet; it requires a holistic approach to health. Key aspects include ensuring a diet rich in essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and proteins, primarily from natural food sources. It's crucial for seniors to consult healthcare providers before starting any supplement regimen to address specific deficiencies safely. Alongside nutrition, incorporating regular physical activity, achieving quality sleep, and managing stress are vital for enhancing overall well-being. By embracing these strategies, seniors can proactively manage their health, improving their immunity and maintaining robust energy levels.